Vacuum Biopsy and Vacuum Excision Biopsy
Vacuum biopsy is a type of needle biopsy which obtains larger tissue samples than that of a core biopsy improving the ability to diagnose the lesion biopsied. It involves inserting a needle with a hollow chamber, under local anaesthetic into the breast tissue and applying a vacuum to cut and suck the tissue into a small chamber at the back of the needle. In this way multiple samples can be taken without the need to re-insert the needle each time.
Vacuum excisional biopsy simply refers to the same technique applied in order to completely remove the lesion. This technique can be utilised to remove lesions up to 15 to 20 mm in size although the larger the lesion the less certainty there is that all of the lesion would be completely removed. This is useful for lesions that are highly likely to be benign such as papilloma’s and fibroadenomas. It also has the advantage of avoiding a general anaesthetic and open biopsy (surgery) which results in a larger scar and potentially more complications of the anaesthesia and surgery
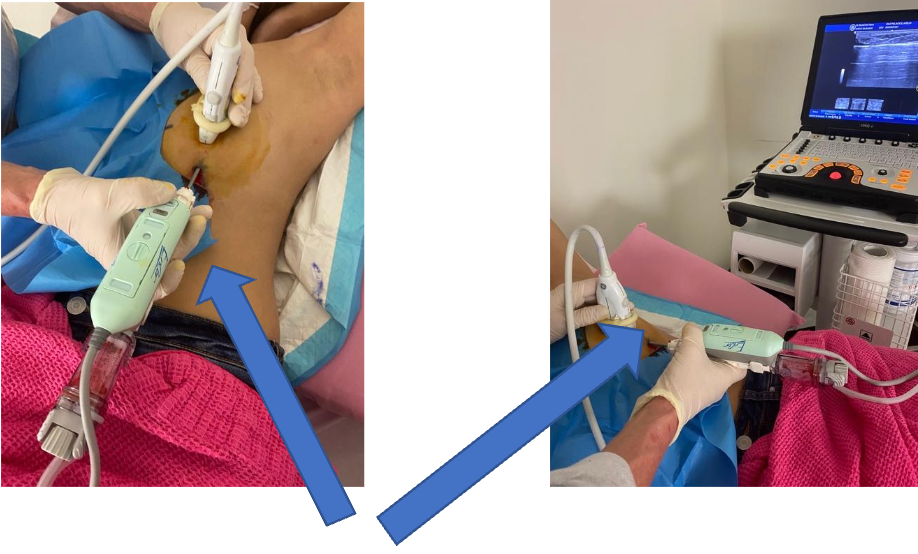
Vacuum excisional biopsy may take up to 20- 30 minutes to perform depending on the size of the lesion. This can be done outside of the hospital in the rooms at Breastcare, through a tiny incision only 3 mm or so in size. Patients should avoid heavy activity for 24 hours. Some bruising is common and occasionally patients may develop a small haematoma which will take a few weeks to completely settle.





